반응형
histogram equalization =
• 영상을 다양한 응용분야에 적합한 형태로 개선하는 것(전처리 과정)
- 특정 영역의 대비(contrast)를 강하게 하거나, 영상의 전체적인 명암의 조절, 혹은, 특정 주파수 대역을 제거하는 방법 등
- 영상의 해석을 용이하게 하거나, 영상 내 특정 정보를 인지 가능하도록 함
- 열화(노이즈) 발생 시 원본 영상 복원


Q. 밝은 사진과 어두운 사진 중 대조를 해줄 때 더 효과적인 것은?
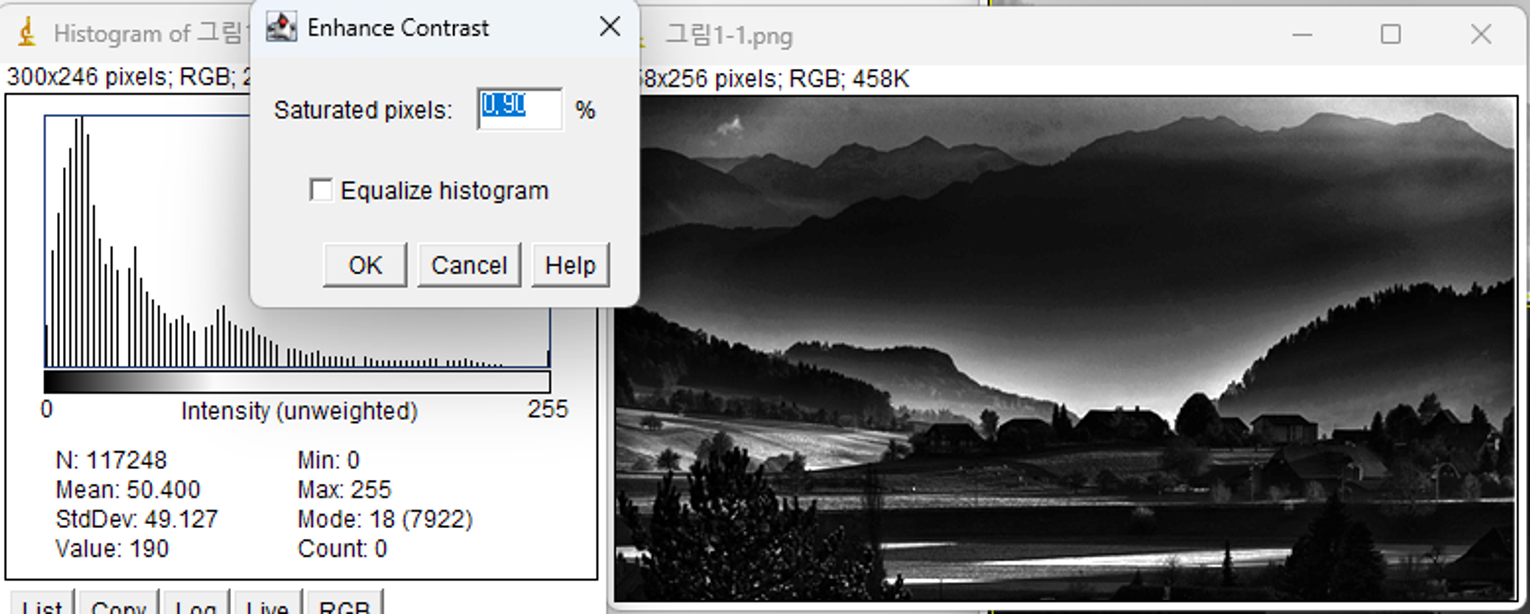

*히스토그램 평활화 과정(smoothing)
1.히스토그램을 생성하고 2.정규화하고 3.정규화된 히스토그램의 누적분포함수를 이용해서 대응 화소값을 생성해준다. 그 후 4.영상의 각 화소 값들을 대응되는 픽셀로 매핑시켜준다.

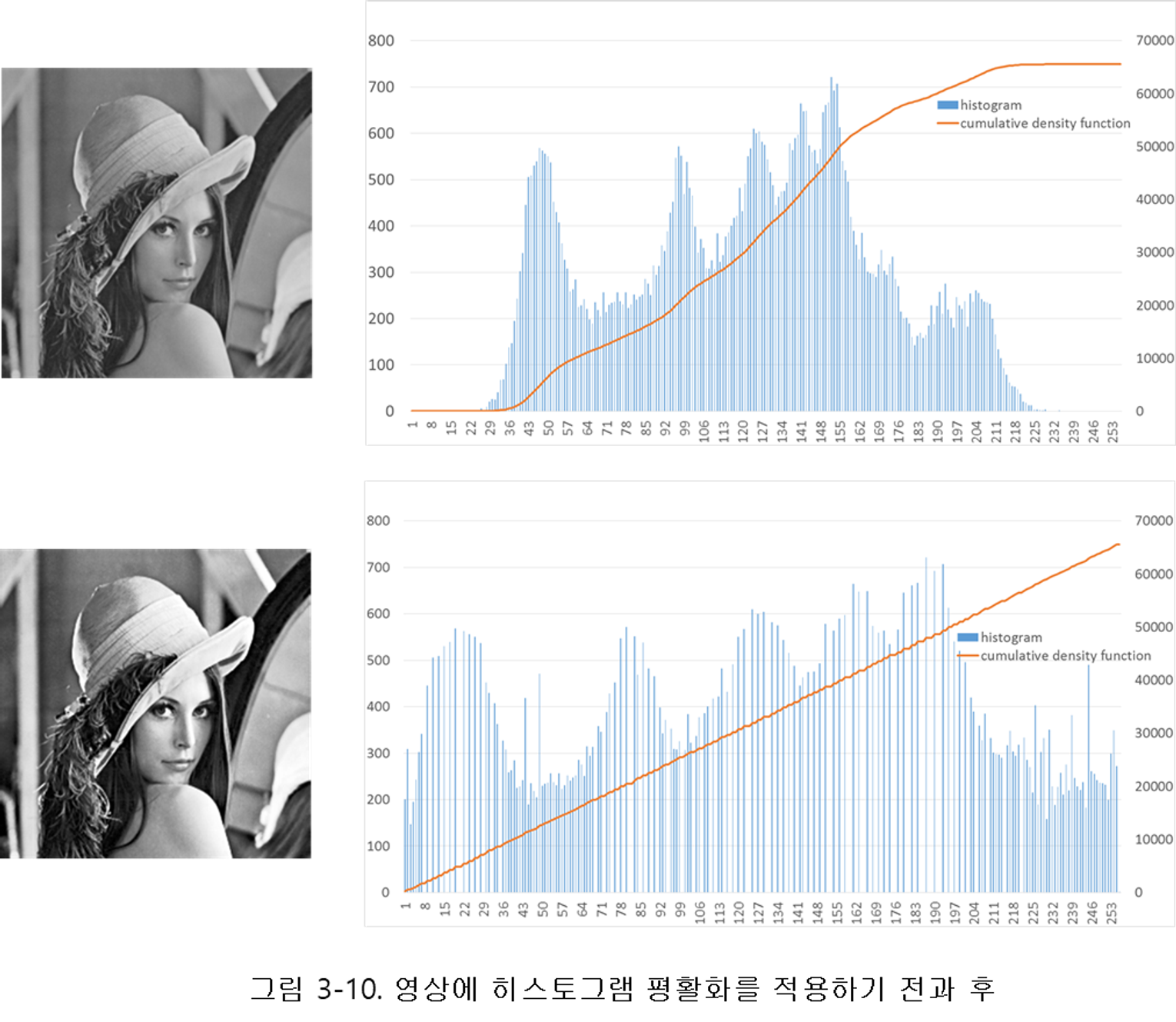
평활화 이후에 확률밀도함수는 선형적으로 바뀌게 됨.



여기까지가 이론이고
*코드
이제 함수들을 라이브러리화 하려고 한다. 이를 위해 ISP.h와 ISP.cpp 클래스를 만들어주고 함수들을 만들어 준다.
//ISP.h
#pragma once
#include "Common.h"
class ISP
{
public:
ISP();
~ISP();
bool Convert_BGR2GRAY(
uchar* pBGR,//color channel, input
int cols,//cols, input
int rows,//rows, input
uchar* pGray//mono channel, output
);
bool Get_Histogram(
uchar * pGray,
int cols,
int rows,
int* pHisto,
int histoSz
);
bool Enhance_HistogramEq(
uchar* pGray,
int cols,//cols, input
int rows,//rows, input
uchar* pGrayEq
);
private:
};
//ISP.cpp
#include "ISP.h"
ISP::ISP()
{
std::cout << "ISP::Ctor" << std::endl;
}
ISP::~ISP()
{
std::cout << "ISP::Dtor" << std::endl;
}
bool ISP::Convert_BGR2GRAY(uchar* pBGR, int cols, int rows, uchar* pGray)
{
if (pBGR == nullptr || pGray == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
for (size_t row = 0; row < rows; row++)
{
for (size_t col = 0; col < cols; col++)
{
int index = (row)*cols + (col);
int val_Y =
0.299 * pBGR[index * 3 + 2]//r
+ 0.587 * pBGR[index * 3 + 1]//g
+ 0.114 * pBGR[index * 3 + 0];//b
pGray[index] = (uchar)(val_Y + 0.5);//올림을 하고 형변환해줘서 오차 최소화
}
}
return true;
}
bool ISP::Get_Histogram(uchar* pGray, int cols, int rows,int*pHisto, int histoSz)
{
if (pGray == nullptr || pHisto == nullptr)//pGray나 pHisto가 뭔가를 가리키고 있지 않다면
{
return false;// false
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < cols*rows; i++)
{
if (pGray[i] >= histoSz)continue;//size 256을 넘는다면 패스 histogram이 터지지 않게 조건 걸어줌
pHisto[pGray[i]]++;//안넘는다면 histo 값 증가
}
return true;
}
//밝은 곳과 어두운 곳의 contrast가 기존에는 180이라면 enhancement 후에는 200정도로 늘어남
bool ISP::Enhance_HistogramEq(uchar* pGray,int cols,int rows,uchar* pGrayEq)
{
if (pGray == nullptr || pGrayEq == nullptr)//pGray나 pGrayEq가 뭔가를 가리키고 있지 않다면
{
return false;// false
}
int length = rows * cols;
const int histoSz = 256;
int histo[histoSz] = { 0, };
Get_Histogram(pGray, cols, rows, histo, 256);
//확률 밀도 함수
int acc[histoSz] = { 0, };
//acc[0]=histo[0]+histo[i] 를 프로그램으로 구현해야함
acc[0] = histo[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < histoSz; i++)
{
acc[i] = acc[i - 1] + histo[i];//이전 확률밀도함수 값에다가 histo값 더해줌.
}
//new look up table 생성... 영상의 각 화소 값들을 새로운 대응값으로 맵핑
int new_Gray[histoSz] = { 0, };
for (size_t i = 1; i < histoSz; i++)
{
new_Gray[i] = static_cast<int>(1.0 * acc[i] * 255 / length);//이전 확률밀도함수 값에다가 histo값 더해줌.
}
for (size_t i = 1; i < length; i++)
{
pGrayEq[i] = new_Gray[pGray[i]]; //계산완료된 값들 Equalization 히스토그램에 맵핑시켜줌
}
//=======csv excel 파일 생성
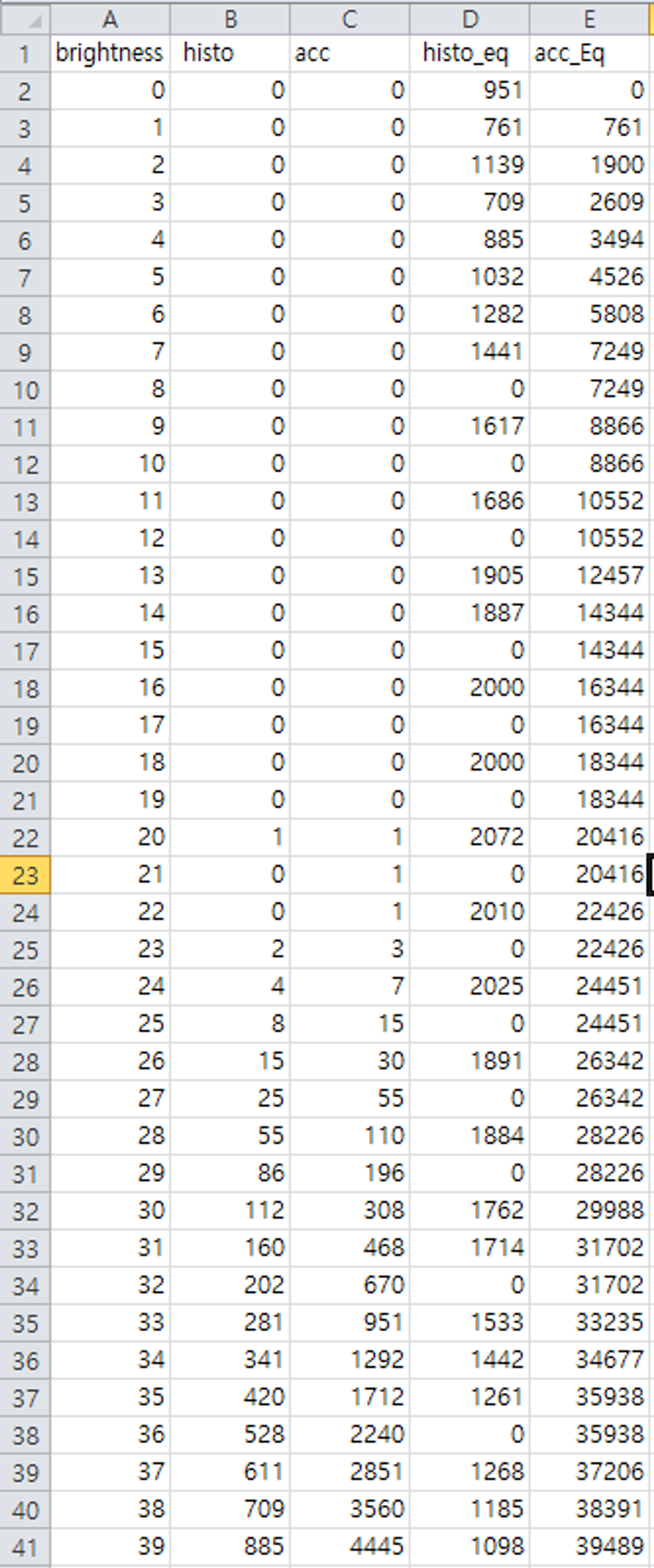
std::ofstream ofile("histogram_eq.csv");
std::string str = "brightness, histo, histo_eq";//제일 윗열에 index 세팅
ofile << str << "\n";//위에 string 이랑 개행 파일에 넣어줌
if (ofile.is_open()) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < histoSz; i++)
{
str = std::format("{}, {}, {}\n", i, histo[i], pGrayEq[i]);
ofile << str;
}
ofile.close();
}
//=======csv excel 파일 생성
return true;
}
//06.ISP_HistoEq.cpp
#pragma once
#include "ISP.h"
int main()
{
std::string fileName = "../thirdparty/opencv_480/sources/samples/data/lena.jpg";
cv::Mat src = cv::imread(fileName, cv::ImreadModes::IMREAD_ANYCOLOR);
uchar* pData = src.data;//color pointer
int length = src.total();//data length=cols*rows
int channels = src.channels();
const int histoSz = 256;
cv::Mat gray_cv = cv::Mat(src.rows, src.cols, CV_8UC1);
cv::Mat gray = cv::Mat(src.rows, src.cols, CV_8UC1);
cv::cvtColor(src, gray_cv, ColorConversionCodes::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
ISP _isp;
_isp.Convert_BGR2GRAY(src.data, src.cols, src.rows, gray.data);
Mat diff = gray_cv - gray;
cv::Mat gray_Eq = cv::Mat(src.rows, src.cols, CV_8UC1);
_isp.Enhance_HistogramEq(gray.data, gray.cols,gray.rows,gray_Eq.data);
return 1;
}

반응형
'Open CV' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [OPENCV-C++ ] blurring (0) | 2023.11.26 |
|---|---|
| [OPENCV-C++ ] gamma correction (2) | 2023.11.25 |
| [OPENCV-C++ ] 영상인식에서 사용하는 색상 모델 (1) | 2023.11.06 |
| [OPENCV-C++ ] HSV threshold 활용해서 원하는 부분만 추출하기 (0) | 2023.11.06 |
| [OPENCV-C++ ] RGB -> YCbCr-> RGB (0) | 2023.11.06 |



